
Hardened steel parts are typically used in rotating applications where high wear resistance and strength is required. The characteristics of case hardening are primarily determined by surface hardness, the effective hardness depth and the depth profile of the residual stress. Gears and engine parts are examples where hardening is used.
Effective case depth is the depth up to a further point for which a specified level of hardness is maintained.
Total case depth is the depth to a point where there is no difference in the chemical or physical properties.
Case depth testing often involves performing a series of hardness impressions from the edge of the specimen towards the center. The hardness progression is plotted on a graph and the distance from the surface to the hardness limit (HL) is calculated.
Vickers Hardness Test
The principle of the Vickers Hardness method is similar to the Brinell method.
The Vickers indenter is a 136 degrees square-based diamond pyramid.
The impression, produced by the Vickers indenter is clearer, than the impression of Brinell indenter, therefore this method is more accurate.
The load, varying from 1kgf to 120 kgf, is usually applied for 30 seconds.
The Vickers number (HV) is calculated by the formula:
HV = 1.854*F/ D²
Where
F-applied load, kg
D – length of the impression diagonal, mm
The length of the impression diagonal is measured by means of a microscope, which is usually an integral part of the Vickers Tester.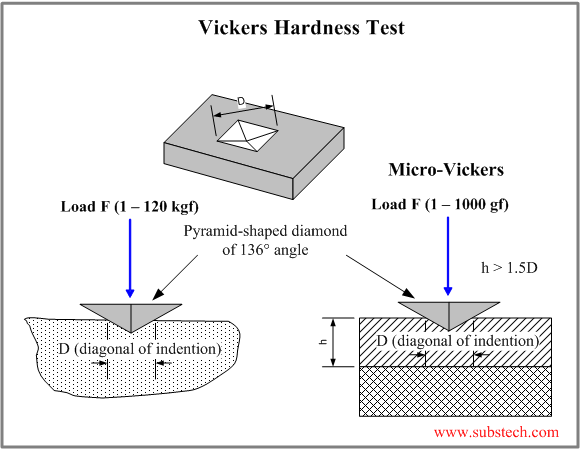


Comments
Post a Comment